Virtual reality has many advantages for training on new medical devices because of its ability to influence our brain and its educational potential. Some companies immediately seized on these possibilities, offering training solutions for surgeons, training organizations, and medical schools.
The objective is to facilitate the acquisition and retention of new knowledge and new gestures by means of an immersive experience.
To help orient you, this article summarizes the various methods, services, budgets, and business principles that exist in this promising market. We begin with a reminder of what we mean by “virtual reality.”
What is virtual reality?
Definition and background
Virtual reality, or VR, is the creation of another reality using various types of content, such as synthetic images or 360° video images. The objective of VR is to dissociate the user from the present by creating an immersive experience.
VR development started mainly in the 1990s and has gradually entered various aspects of our daily life: Google Street View, video games, and virtual apartment tours are all examples of how this new, multimodal technology is used.
In the field of education, VR is particularly promising because it offers a way to create an immersive experience that can considerably improve learning quality. This is what needs to be retained from the various alternatives offered in this field, their pedagogical advantages and drawbacks, and their budget.
Synthetic images: good environmental interaction, but expensive
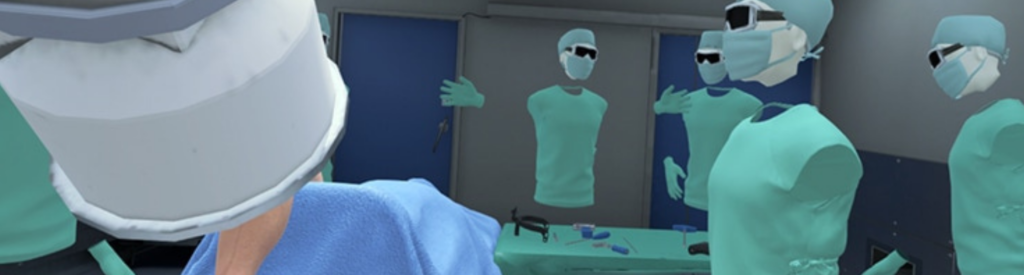
Synthetic images are created by using graphics and IT development to construct an artificial universe that is as realistic and convincing as possible. They are used for video games, for example, but also for flight simulators. Here is a summary of their advantages and drawbacks in terms of training:
- Advantages:
a) When it’s well done, it gives the impression of truly diving into a new universe.
b) It’s possible to interact with this virtual environment, which facilitates learning.
c) It’s a good alternative when filming and projecting a situation isn’t possible.
- Drawbacks:
a) The manufacturing cost is the main drawback. It takes a large budget to produce a high-definition rendering that provides a realistic experience with synthetic images (situational fidelity and realistic images).
b) Manufacturing time: after the graphic itself is created, development takes about six months.
360° video images: more realistic but less immersive
This is like visiting an apartment virtually or taking a stroll with Google Street View. Several cameras are placed next to one another to give a faithful rendering of a given environment. The subject is an observer of this environment.
- Advantages:
a) Realism: The proposed environment is close to reality since it involves “real life,” which helps people project themselves into a learning context or situation.
b) Manufacturing time: It is considerably faster to produce than synthetic images (since it involves filming real-life situations).
c) Flexibility of use: It requires less equipment than synthetic images do.
- Drawbacks:
a) The main drawback is that learners are in the observer position, so that they can watch what is being done but cannot do it themselves. This results in fewer interactions for learners.
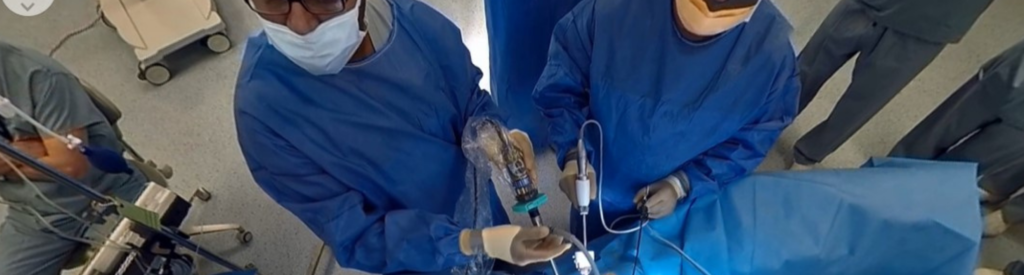
180° video images with a first-person point of view for an optimal experience
This procedure uses cameras for 180° immersion in the learning situation. Why 180°? Because the instructor (the surgeon, in this case) has a camera, which films the whole procedure or learning situation from a first-person perspective.
- Advantages:
a) The combination of the immersive plunge and the realism of video
b) Maximum stimulation of learning capacity from the first-person point of view combined with interaction with the proposed environment
c) The same cost and manufacturing time as for 360° videos
It’s all a matter of perspective: how VR optimizes learning through the immersive experience
Surgical training: not mechanical repetition but human involvement
In surgery there is no standardized gesture or predefined control of all the parameters. This demands both complete mastery of one’s art and the ability to deal with unforeseeable situations. This also assumes prioritizing learning that immerses the future surgeons in real-life situations as much as possible to prepare them as much as possible for the unexpected.
The importance of the first-person point of view
When we learn to ride a bike, we can read a book about how to get on the seat, hold the handlebar, etc. We can also pedal on a real bicycle and see what happens. The same principle applies to VR: by using first-person immersion, the brain works by actually experiencing the learning experience, which greatly improves memorization time and efficiency compared with being in an observer position.
Revinax offers blended learning
Blended learning is a learning technique that combines different tools, methods, and types of learning for the best possible result. The idea is to cognitively structure learning to obtain the most complete training solution possible. For this reason, Revinax offers a first-person immersive learning experience.
- With the VR headset, learners experience the procedure as if they were the KOL, thanks to 180° video immersion in the surgical situation.
- The additional information and structuring of each step of the procedure into chapters lets the brain find the information it needs more quickly.
- What is the idea behind that? Maxime Ros, a neurosurgeon himself with a PhD in education, had a hunch that performing a technical gesture in an immersive environment would allow the brain to integrate this gesture as if it were real. Since then, his hunch has been scientifically validated. Memorization time is shortened enormously.
- Tutorials created in this way are stored on an online platform with secure access. This knowledge library allows all of the automated cognitive processing to be reactivated on demand and reinforces memorization. The budget for this is up to ten times less than for synthetic images.
We see then that virtual reality can take on different forms, depending in the purpose for which it is used. In surgery, it offers infinite learning possibilities, provided that the constraints and characteristics specific to medical learning are integrated into the creation and use of these training tutorials.





